
Budgeting is one of the most important financial skills you can develop, yet it’s often misunderstood or avoided. Whether you’re trying to save for a big purchase, pay off debt, or simply gain better control of your finances, creating and sticking to a budget is essential. A well-planned budget allows you to track your spending, manage your money more effectively, and make informed financial decisions.
In this guide, we’ll break down the essentials of budgeting, offer tips for creating a realistic budget, and show you how to stick to it so you can achieve your financial goals.

What is Budgeting?
At its core, budgeting is the process of creating a plan for how to spend your money. It helps you balance your income with your expenses, ensuring that you’re not spending more than you earn. A budget allows you to see where your money is going and helps you prioritize your spending based on your financial goals.
A good budget can also prevent you from living paycheck to paycheck and can give you peace of mind knowing that your finances are under control.

Why is Budgeting Important?
Budgeting is important for several reasons:
- Helps you avoid overspending: Without a budget, it’s easy to spend money without realizing where it’s going. A budget helps you keep track of your spending and ensure you’re living within your means.
- Allows you to save for the future: A budget can help you set aside money for future goals, such as buying a house, traveling, or saving for retirement.
- Reduces financial stress: Knowing exactly where your money is going can reduce the anxiety and uncertainty that often comes with managing personal finances.
- Helps you pay off debt: A budget allows you to allocate funds specifically for paying off debts, helping you get out of financial trouble faster.
- Encourages mindful spending: When you stick to a budget, you become more mindful of how you’re spending your money, which can lead to better financial habits over time.

Step 1: Track Your Income and Expenses
The first step in creating a budget is to get a clear picture of your current financial situation. To do this, you’ll need to track your income and expenses.
Track Your Income
Your income includes any money you receive regularly, such as:
- Your salary or wages
- Freelance or side gig income
- Government benefits or subsidies
- Investment income
- Any other sources of regular income
Make sure to use your net income (take-home pay after taxes and deductions) when creating your budget.
Track Your Expenses
Next, you’ll need to track your monthly expenses. Expenses typically fall into two categories:
- Fixed expenses: These are expenses that remain the same each month, such as rent, mortgage payments, car payments, insurance, credit cards, and utilities.
- Variable expenses: These are expenses that fluctuate from month to month, such as groceries, entertainment, dining out, and transportation.
To get an accurate picture of your spending, review your bank and credit card statements for the last three months. Categorize your expenses, such as:
- Housing
- Food and groceries
- Transportation (gas, public transportation, car maintenance)
- Utilities (electricity, water, internet)
- Debt repayment (student loans, credit cards)
- Savings and investments
- Health care (insurance, medications)
- Entertainment and leisure (movies, dining out, subscriptions)
By tracking your income and expenses, you’ll be able to identify areas where you may be overspending and where you can cut back.

Step 2: Set Financial Goals
Once you have a clear understanding of your income and expenses, the next step is to set financial goals. Having specific goals will help guide your budgeting decisions and keep you motivated to stick to your budget.
There are two types of financial goals:
- Short-term goals: These are goals you want to achieve within the next year, such as saving for a vacation, paying off a credit card, or building an emergency fund.
- Long-term goals: These are goals that may take several years to achieve, such as saving for a down payment on a house, paying off student loans, or saving for retirement.
When setting financial goals, make sure they are SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound). For example, instead of saying, “I want to save money,” a SMART goal would be: “I want to save $5,000 for a down payment on a house within the next 12 months.”
Step 3: Create a Budget Plan
With your income, expenses, and goals in mind, you’re ready to create your budget plan. Follow these steps to create a realistic budget that works for you.
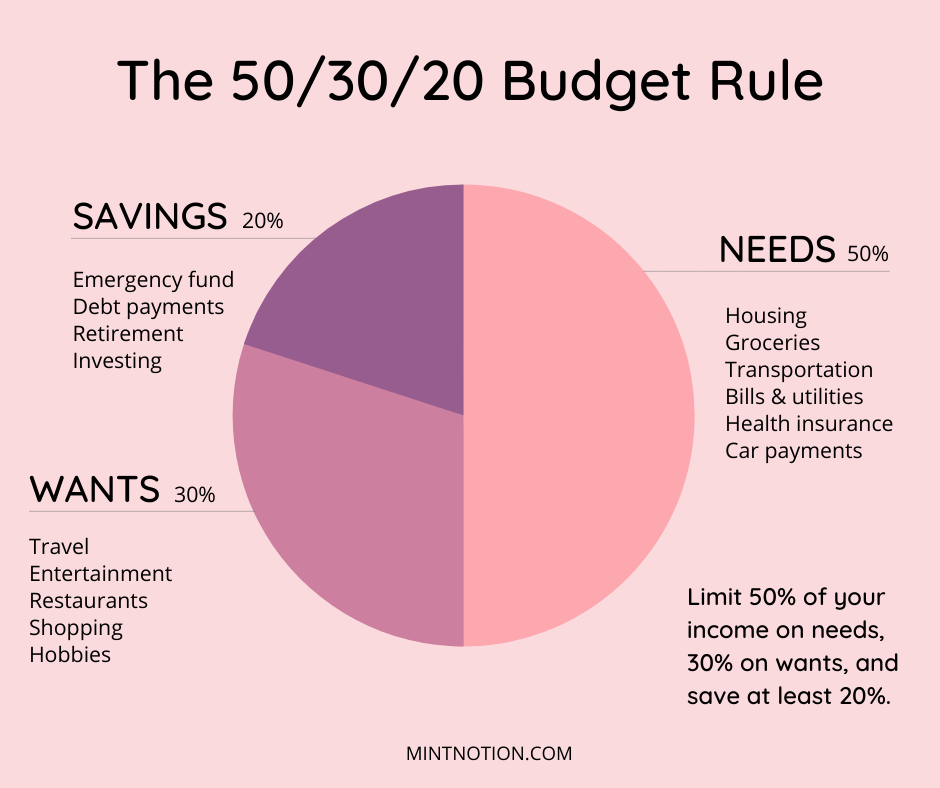
Use the 50/30/20 Rule
One of the most popular budgeting methods is the 50/30/20 rule. This rule suggests allocating your income into three main categories:
- 50% for needs: These are essential expenses, such as housing, utilities, groceries, and transportation.
- 30% for wants: These are non-essential expenses, such as dining out, entertainment, travel, and hobbies.
- 20% for savings and debt repayment: This includes contributions to your savings account, emergency fund, retirement fund, and payments toward debt.
This method is a great starting point, but you can adjust the percentages based on your personal situation. For example, if you’re aggressively paying off debt, you may want to allocate more than 20% toward debt repayment.

Create Budget Categories
Organize your spending into categories based on your lifestyle and financial goals. For example, you could have categories for:
- Rent or mortgage
- Utilities
- Groceries
- Dining out
- Transportation
- Health care
- Subscriptions
- Entertainment
- Debt payments
- Savings
Assign a spending limit for each category based on your income and financial priorities. Be realistic and flexible when setting these limits.
Step 4: Monitor and Adjust Your Budget
Creating a budget is just the first step. To ensure your budget is effective, you’ll need to monitor your spending regularly and make adjustments as needed.
Track Your Spending
Keep track of your spending in each category throughout the month. You can do this manually with a spreadsheet, or use budgeting apps like Mint, You Need a Budget (YNAB), or EveryDollar. These tools make it easy to monitor your spending in real-time and ensure you stay within your budget limits.
Review and Adjust Your Budget
At the end of each month, review your budget to see how well you stuck to your plan. Did you overspend in certain categories? Were you able to save as much as you planned? Use this information to make adjustments for the following month.
Life is unpredictable, and your financial situation may change over time. Your budget should be flexible enough to accommodate unexpected expenses, such as medical bills or car repairs, as well as changes in income.

Step 5: Build an Emergency Fund
A key component of any budget is having an emergency fund. An emergency fund is a savings account specifically designated for unexpected expenses, such as medical emergencies, car repairs, or job loss. Having an emergency fund can prevent you from going into debt when life throws you a curveball.
Experts recommend having at least three to six months’ worth of living expenses saved in your emergency fund. If you don’t have an emergency fund yet, prioritize saving for one by allocating a portion of your budget to it each month.
Step 6: Stay Motivated and Accountable
Sticking to a budget can be challenging, but staying motivated is key to long-term success. Here are some tips to help you stay on track:
- Celebrate small wins: When you reach a financial milestone, such as paying off a credit card or hitting a savings goal, celebrate your achievement. This will keep you motivated to continue budgeting.
- Find an accountability partner: Share your budgeting goals with a friend, family member, or financial advisor who can help keep you accountable.
- Review your goals regularly: Keep your financial goals in mind and review them regularly to remind yourself why you’re budgeting in the first place.

Budgeting is a powerful tool that can help you take control of your finances, reduce stress, and achieve your financial goals. By tracking your income and expenses, setting clear financial goals, and sticking to your budget plan, you can build a more secure financial future. Remember, budgeting is a process, and it may take time to get it right—but with persistence and discipline, you can gain control over your money and live a more financially empowered life.

